Griffin Gaming Partners & Rendered.VC - Game Development Trends in 2023
A giant and very insightful lookout of the industry. Must read.
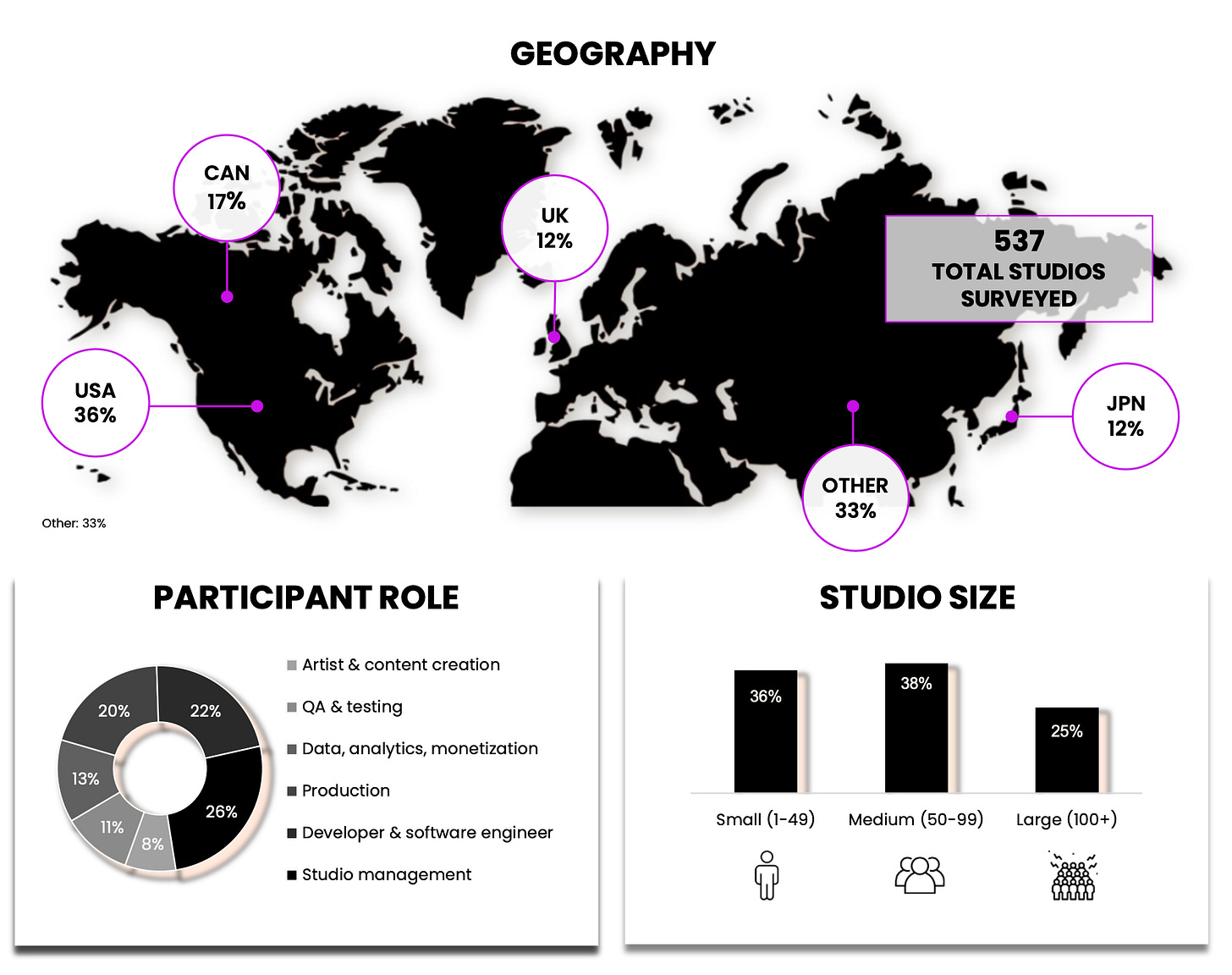
537 studios from different countries participated in the survey. Businesses of various sizes were surveyed; among the respondents were management, developers, analysts, and professionals from other fields.
40% of respondents develop games on Unreal Engine; 36% on Unity; 19% on their own engine. 70% develop games for PC; 56% for consoles and mobile devices; 48% for web platforms.
General trends
77% of studios reported that development costs continue to rise.
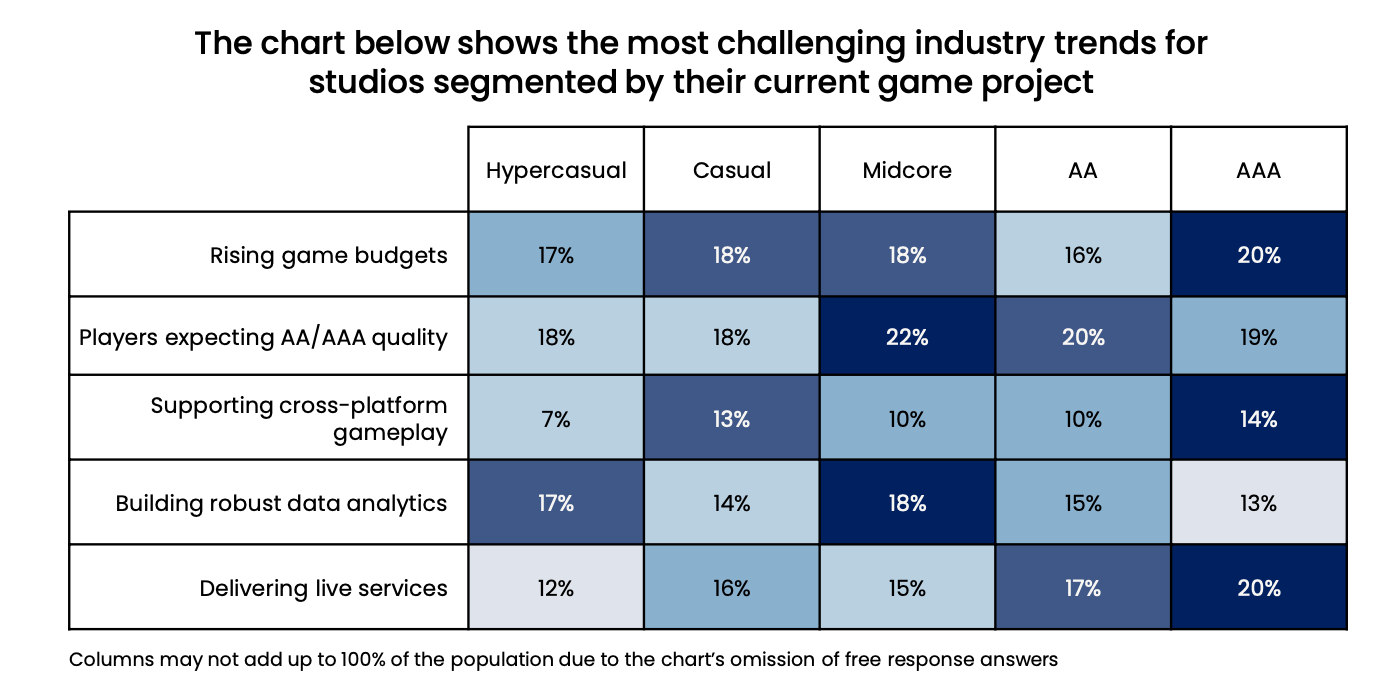
According to developers' perceptions, costs for programmers, game designers, QA, and testing are increasing the most.
65% of developers are working on projects that will receive regular updates after release. 30% are considering this.
88% of studios actively consider new technologies to improve their workflow.
Development Trends
Development costs are rising due to increasing complexity and demands of games. 74% of artists are confident that the production of 3D art is becoming more expensive. Additionally, there are numerous issues related to file management, libraries, and collaborative work.
79% of developers face long build times - over 10 minutes. This slows down all processes within the team. Teams would like to see a faster and more iterative process.
Testing is becoming increasingly difficult, especially noticeable in large projects and games with complex operations.
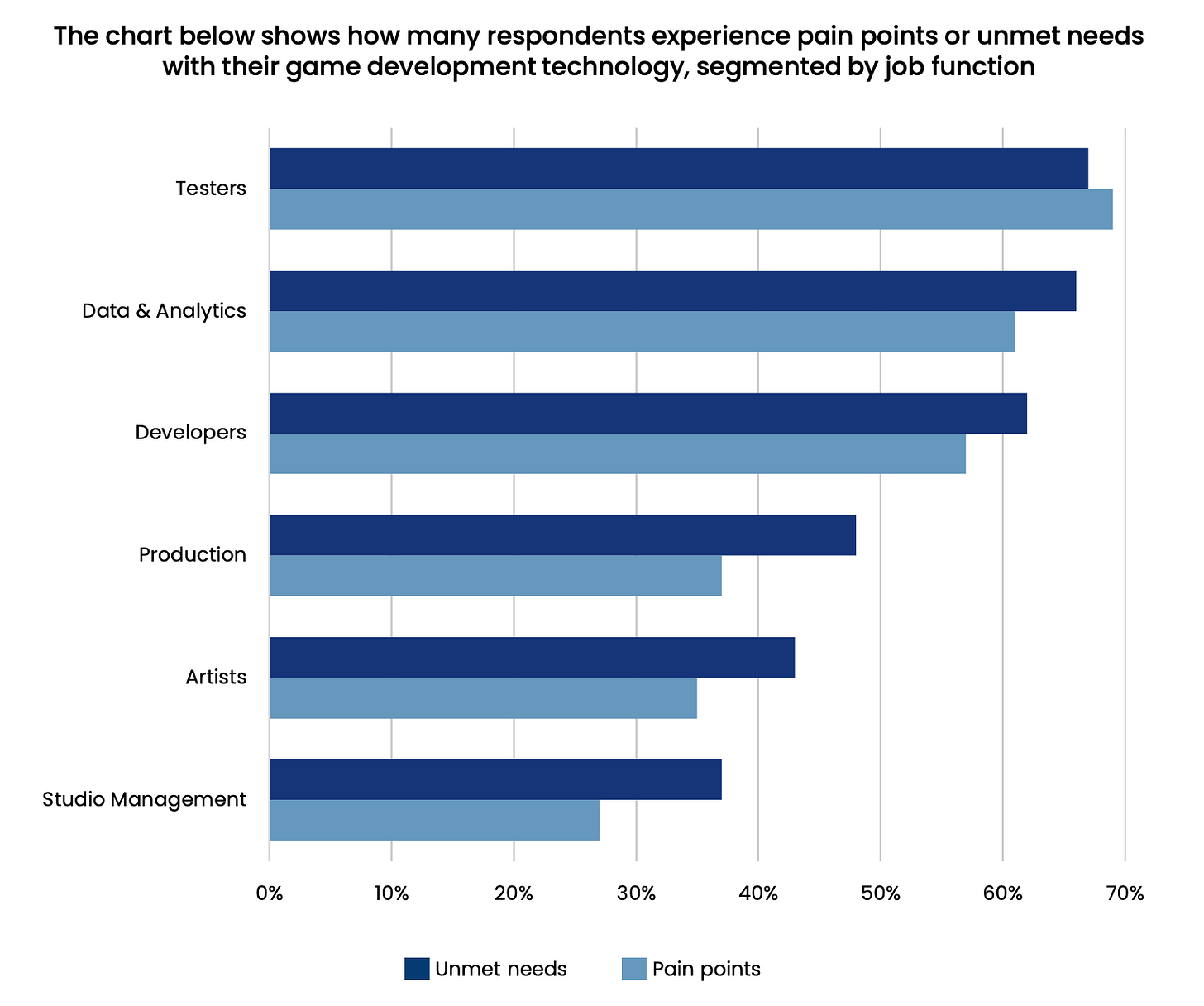
32% of teams encounter problems working with analytics. The issue is not just collecting data but working with it - gathering useful numbers and interpreting them correctly is challenging.
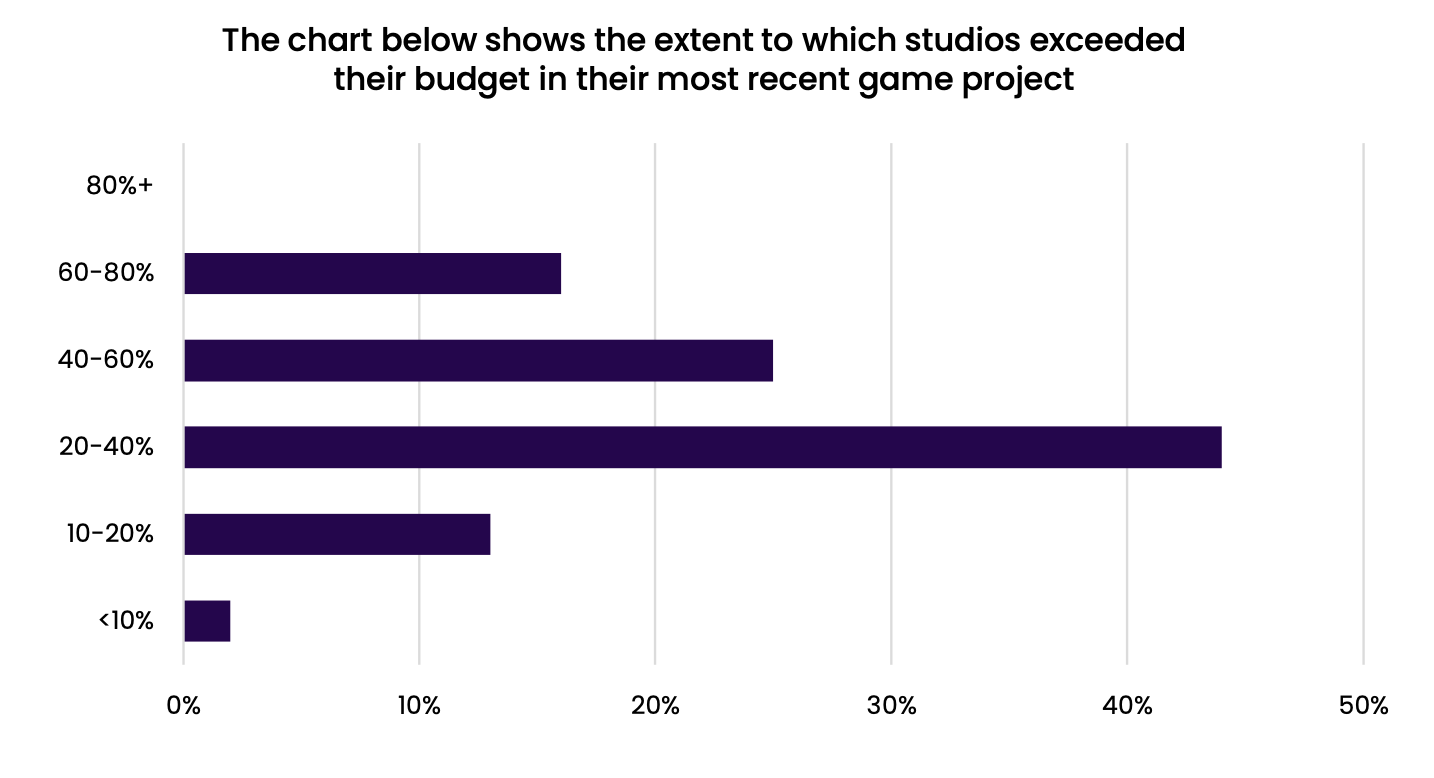
Most teams have significant budget planning issues. 44% of studios increased their initial budget by 20-40%. 25% increased it by 40-60%. 16% of studios had to increase the budget by 60-80%. For 13% of teams, the increase is minor - by 10-20%. And only 2% saw budget growth of less than 10%.
One of the sources of budget problems is incorrect deadlines. In the case of programmers, only 12% deliver tasks on time; among game designers, it's 15%.
The problem of technical legacy is most common in large studios. Over 55% of large companies suffer from it.
Product Processes
56% of producers would like to release game updates on a weekly or biweekly basis.
68% of producers believe their product pipelines are not suitable for service games. The problem is that developing a game and supporting it are two different development approaches.
For leaders in service games, updates are released almost daily (compared to 1-2 times a week on average in the market); planning accuracy is above 75% (compared to 3% on average in the market); significant errors are below 5% (compared to 61% on average in the market).
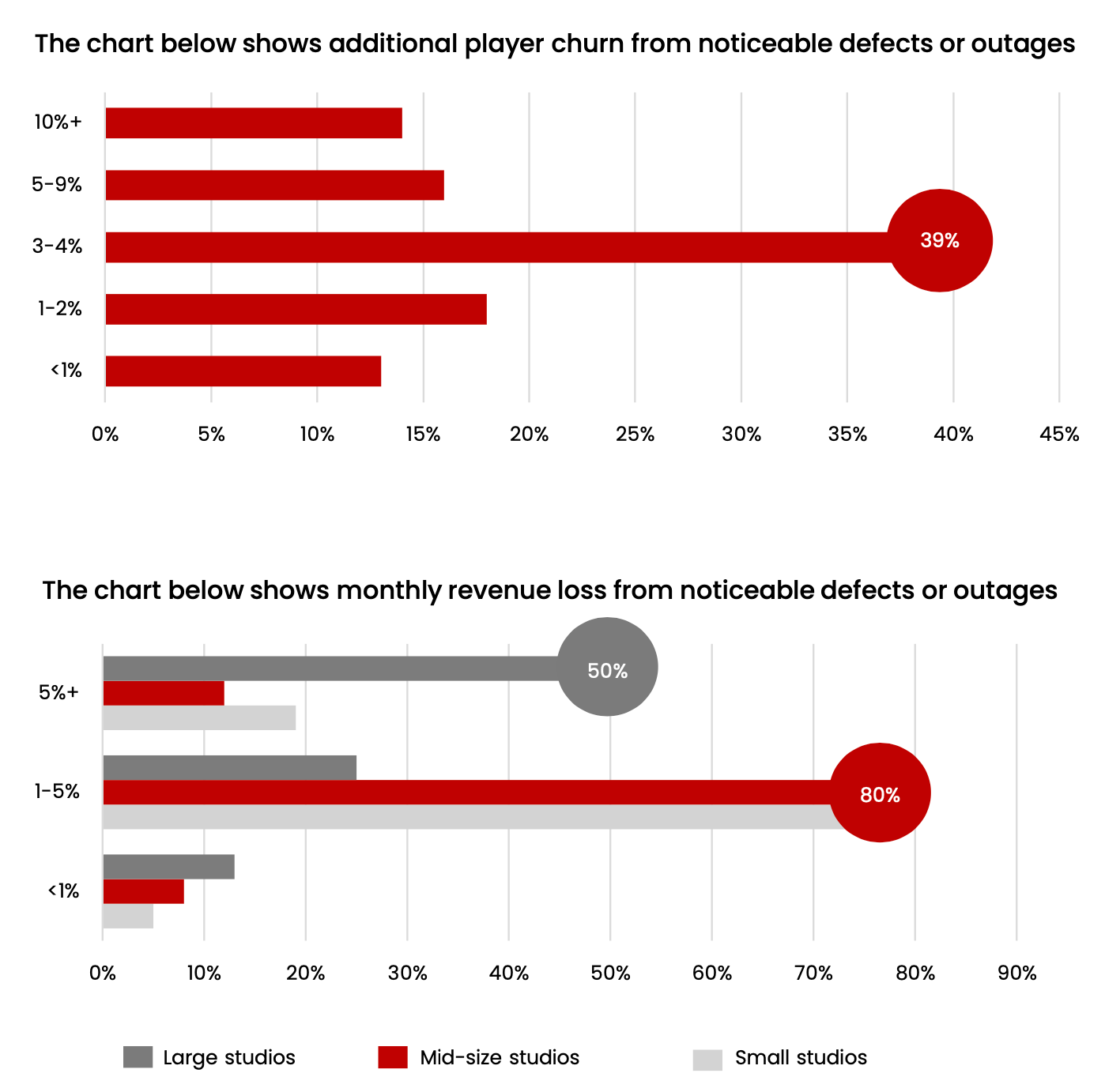
Bugs or technical unavailability of the game affect audience and revenue. For half of large companies, technical problems lead to a revenue decrease of 5% or more. For 14% of studios, user churn increases by more than 10%.
Tech Development Trends
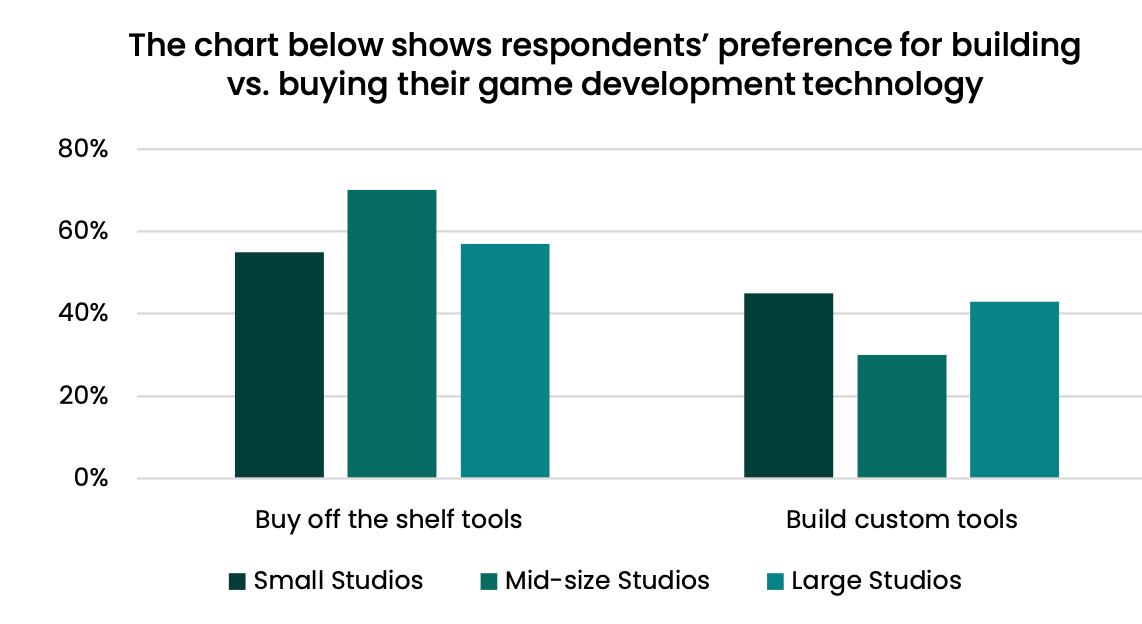
65% of studios plan to use more off-the-shelf solutions rather than building their own.
However, the trend is unclear as there is no comparison with previous years.
One of the main tasks of studios at the moment is standardizing the technical stack and reducing time-to-market. In addition, large companies express interest in quality technical support and support for old products. Among the main reasons for creating custom solutions are the lack of functionality in market solutions, risks of vendor dependence, and price.
94% of studios plan to increase their use of cloud infrastructure.
52% of artists believe that within 2 years AI will be able to produce the same result as the average artist can now.